top of page
Environmental education
For schools
The Reserve is open to schools and offers personalized itineraries, guided tours, and educational activities for preschool, elementary, and middle school classes. Contact the Groane Park office for information on large groups.

Download the factsheet and discover the curiosities that the Reserve contains
For schools
The Groane Park and the Brughiera Briantea are relaunching "Adopt a Tree." The slogan perfectly explains the purpose of this campaign: "Groane Park is for your children and your children's children. Have you ever thought about it? Adopt a tree or a forest and dedicate it to those you love most!" How does it work? Simple. Visit the Groane Park headquarters (or one of the organization's events) in Solaro, at Via della Polveriera 2 (on the Monza-Saronno highway) and let the reception know you want to join the "Adopt a Tree" campaign. With a donation of €5, you can adopt a tree and receive one of our freebies along with an adoption certificate.
With this initiative, it is also possible to adopt a tree within the "Fontana del Guercio" Reserve.
For more information, contact the park authority or visit the website: https://www.parcogroane.it/natura/adotta-un-albero/
The phytoremediation plant
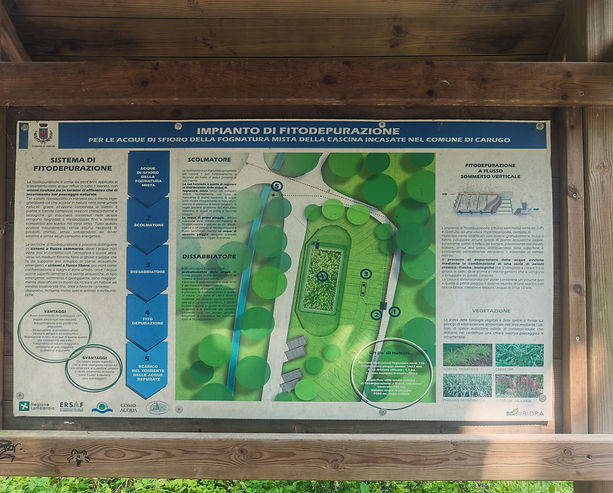
Phytoremediation has been used for wastewater treatment worldwide for thirty years, achieving excellent results in terms of both efficiency and integration into the natural landscape. Located outside the Reserve, it allows for the treatment of excess water from Incasate.
These systems reproduce, in a more or less engineered manner, what happens naturally in natural wetlands: thanks to the combined action of bacteria and plants, and through complex chemical, physical, and biological reactions, the pollutants contained in the water are degraded and metabolized until they are suitable for discharge into bodies of water. All this occurs naturally, without the need for chemicals, without byproducts to dispose of, and without any energy consumption.
Phytoremediation techniques can be divided into submerged flow systems, where water never comes into contact with the atmosphere and flows through a filter medium of gravel and sand that supports the growth of emergent aquatic plants, and free-flow systems, which are more similar in structure to ponds and wetlands, where water flows surface-level and the aquatic plants—emergent, submerged, and floating—are more diverse, recreating a habitat with high biodiversity that, in addition to promoting purification processes, attracts numerous animal and bird species.
bottom of page

